FortiOS 6.4.4 > ikev2 (dynamic)
Configuring Fortinet Next Generation Firewall
Version tested: Fortinet Next Generation Firewall version FortiOS 7.2
In this section we will refer to the configuration file you obtained from our UCCS Onboarding teams as “template conf” and will explain how to use its contents for configuring FortiOS 7.2.
As a reference for this guide, here is the full AWS file: FortiOS 6.4.4+ ikev2 (dynamic).txt
Interface names in AWS template are too long and need to be adjusted.
Create VPN Tunnels
To create VPN Tunnels go to VPN > IPSec Tunnels > click “Create New”
The VPN Creation Wizard appears, select “Custom” and click Next:
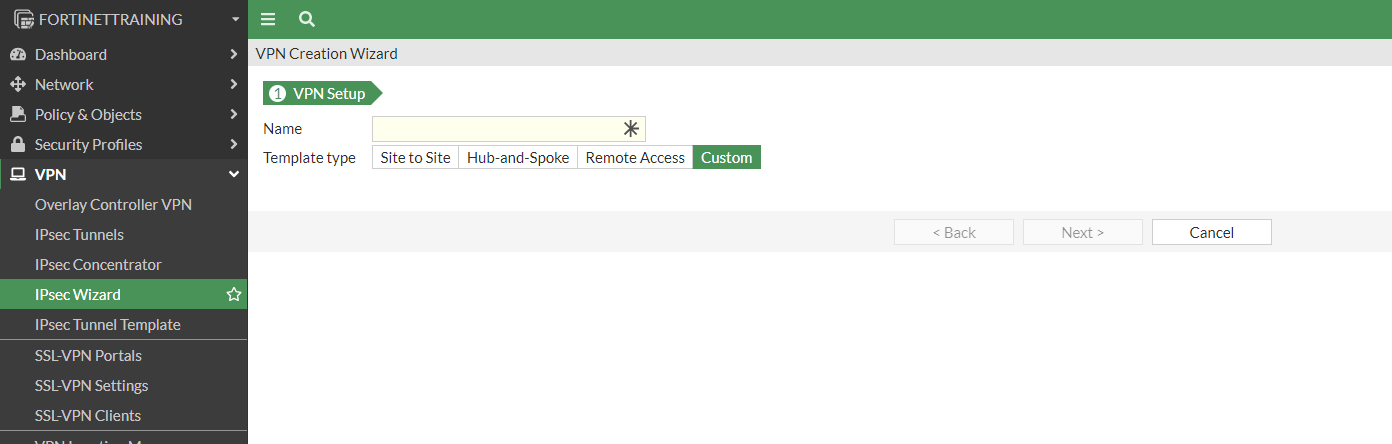
Configure the tunnel as specified in the template conf #1 Internet Key Exchange (IKE) Configuration
a. IP Version: IPv4b. Remote Gateway: Static IP Addressc. IP address: 3.126.101.234d. Local Interface: wan1e. Local Gateway: Select Specify and enter WAN port IP (Public IP)f. Dead Peer Detection: Enable by selecting On Idle/ On Demandg. Authentication Method: Pre-shared Keyh. Pre-Shared Key: knJNjlMhl9b1Ydt8V7xHxPeGp_gRGIvFi. IKE Version: 2Phase 1 Proposal:j. Encryption: aes128k. Authentication: sha1l. DH group: 2 ! and deselect 5m. Keylife: 28800 seconds
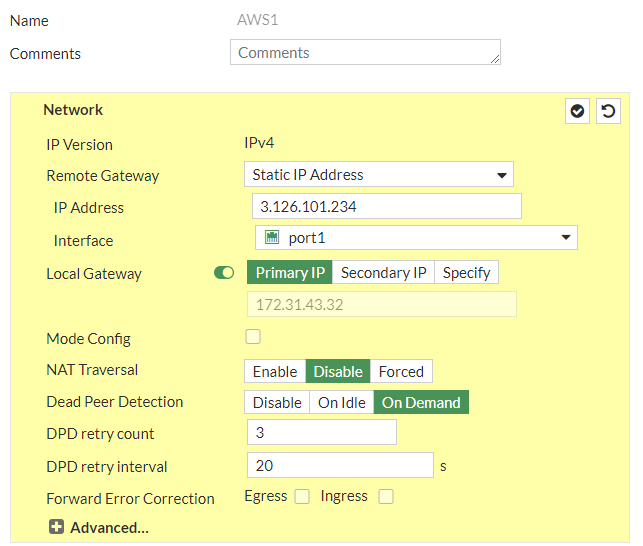
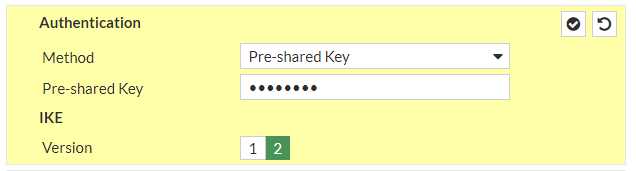
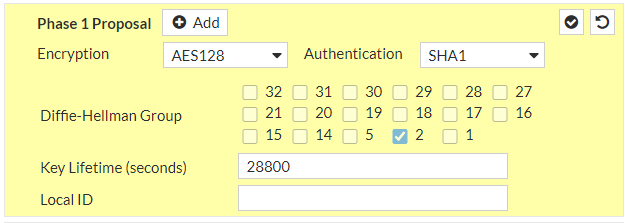
and continue with #2: IPSec Configuration
Under Phase 2 Selectors --> New Phase 2a. Name: vpn-093bd262ad8d9a8b4-0b. Local Address: LAN subnet behind Fortigate/0.0.0.0/0c. Remote Address: AWS Private Subnet/0.0.0.0/0Under Advancedd. Encryption: aes128e. Authentication: sha1f. Select Enable Replay Detectiong. Select Perfect Forward Secrecyh. DH Group: 2 ! and deselect 5i. Keylife: 3600 secondsj. Enable Auto-negotiate ! Autokey Keep Alive is enabled automatically when Auto-negotiate is enabledk. Click Ok
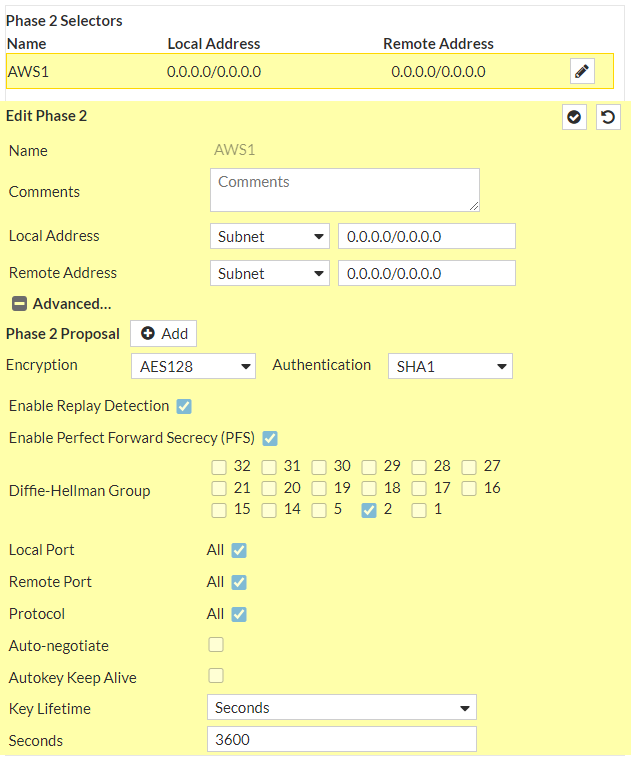
and let’s do the same also for the IPSec Tunnel #2
a. IP Version: IPv4b. Remote Gateway: Static IP Addressc. IP address: 35.156.84.84d. Local Interface: wan1e. Local Gateway: Select Specify and enter WAN port IP (Public IP)f. Dead Peer Detection: Enable by selecting On Idle/ On Demandg. Authentication Method: Pre-shared Keyh. Pre-Shared Key: UUegcCakIsG7BnxbhROo0S0ZPUYOvEYSi. IKE Version: 2Phase 1 Proposal:j. Encryption: aes128k. Authentication: sha1l. DH group: 2 ! and deselect 5m. Keylife: 28800 seconds
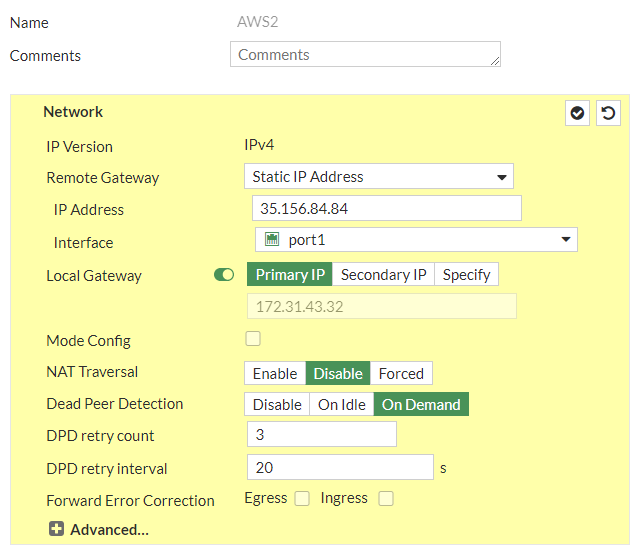
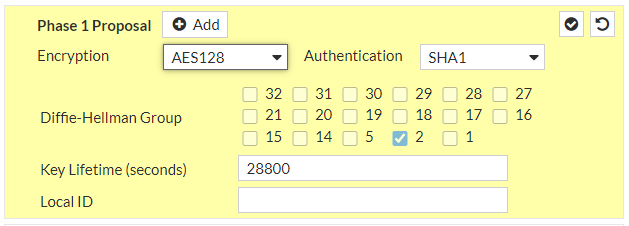
and
Under Phase 2 Selectors --> New Phase 2a. Name: vpn-093bd262ad8d9a8b4-1b. Local Address: LAN subnet behind Fortigate/0.0.0.0/0c. Remote Address: AWS Private Subnet/0.0.0.0/0Under Advancedd. Encryption: aes128e. Authentication: sha1f. Select Enable Replay Detectiong. Select Perfect Forward Secrecyh. DH Group: 2 ! and deselect 5i. Keylife: 3600 secondsj. Enable Auto-negotiate ! Autokey Keep Alive is enabled automatically when Auto-negotiate is enabledk. Click Ok
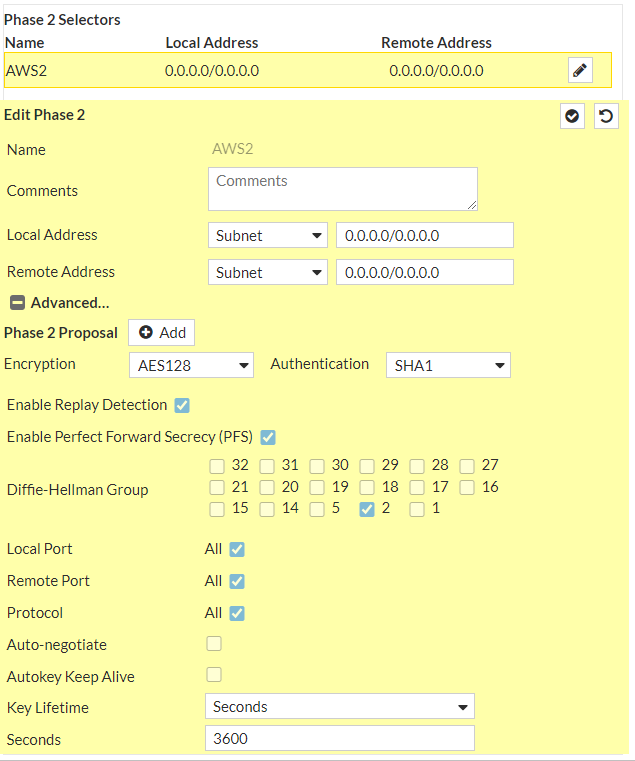
Configure Tunnel interfaces
A tunnel interface is configured to be the logical interface associated with the tunnel.
As defined in #3: Tunnel Interface Configuration we should configure the addresses accordingly:
a. IP : 169.254.92.226b. Remote IP: 169.254.92.225/30c. Select Pingd. Administrative Status: Upe. Select Ok.
Go to Networks > Interfaces > expand the physical interface attached to the tunnel interfaces and click on those tunnel interfaces:
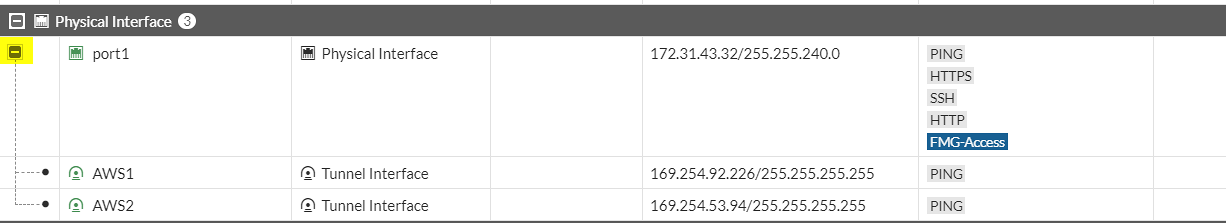
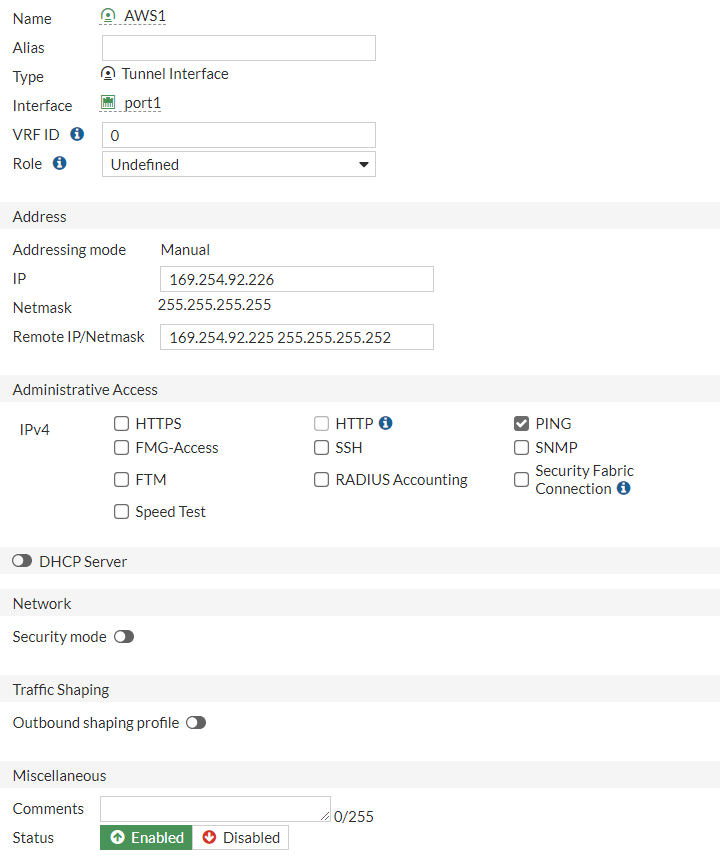
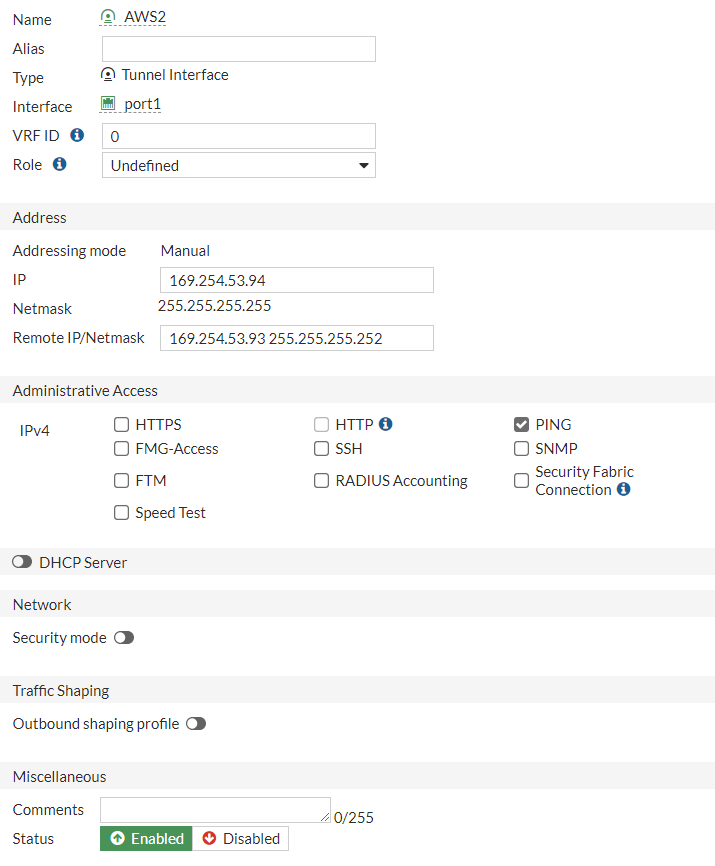
do the same for the second interface:
a. IP : 169.254.53.94b. Remote IP: 169.254.53.93/30c. Select Pingd. Administrative Status: Upe. Select Ok.
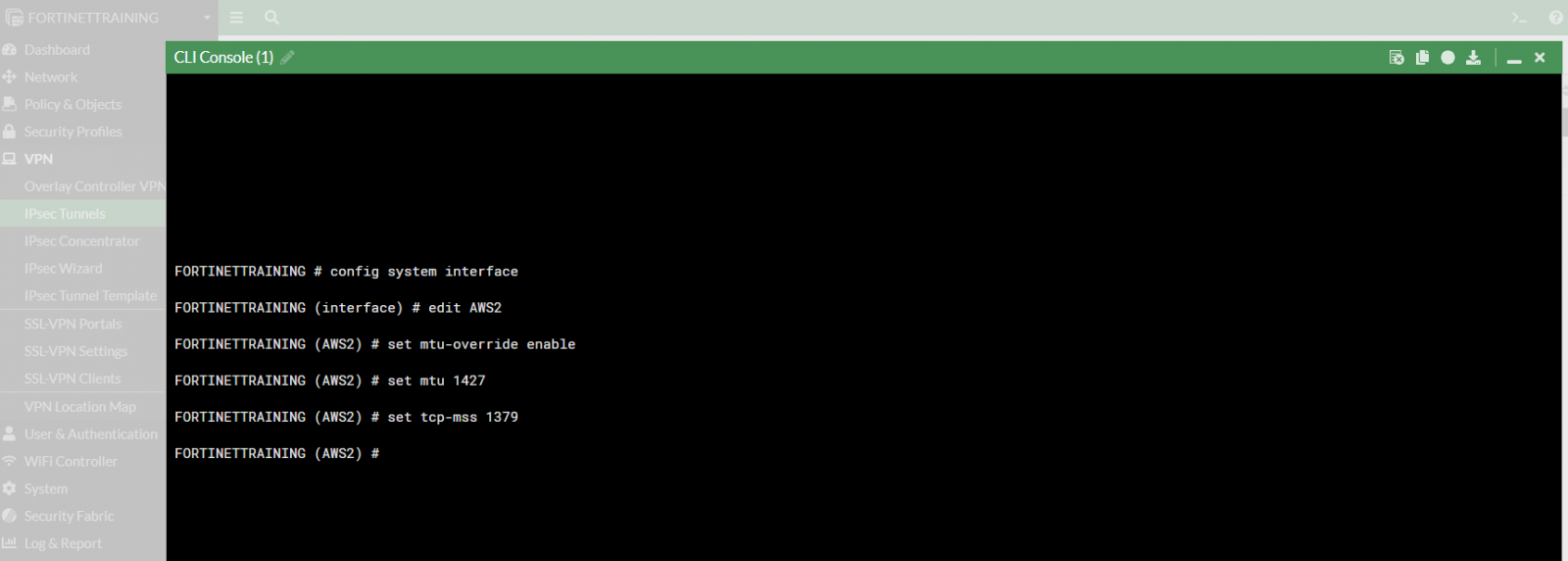
To set the MTU and MSS as reported in the template conf:
!You can set MTU and MSS on the tunnel by performing this from the CLI:
config global config system interface edit "vpn-093bd262ad8d9a8b4-0" ! This name will be the same as the VPN tunnel name set mtu-override enable set mtu 1427 set tcp-mss 1379 nextend
Open the CLI Console
and configure both interfaces (AWS1 and AWS2):
Configure BGP:
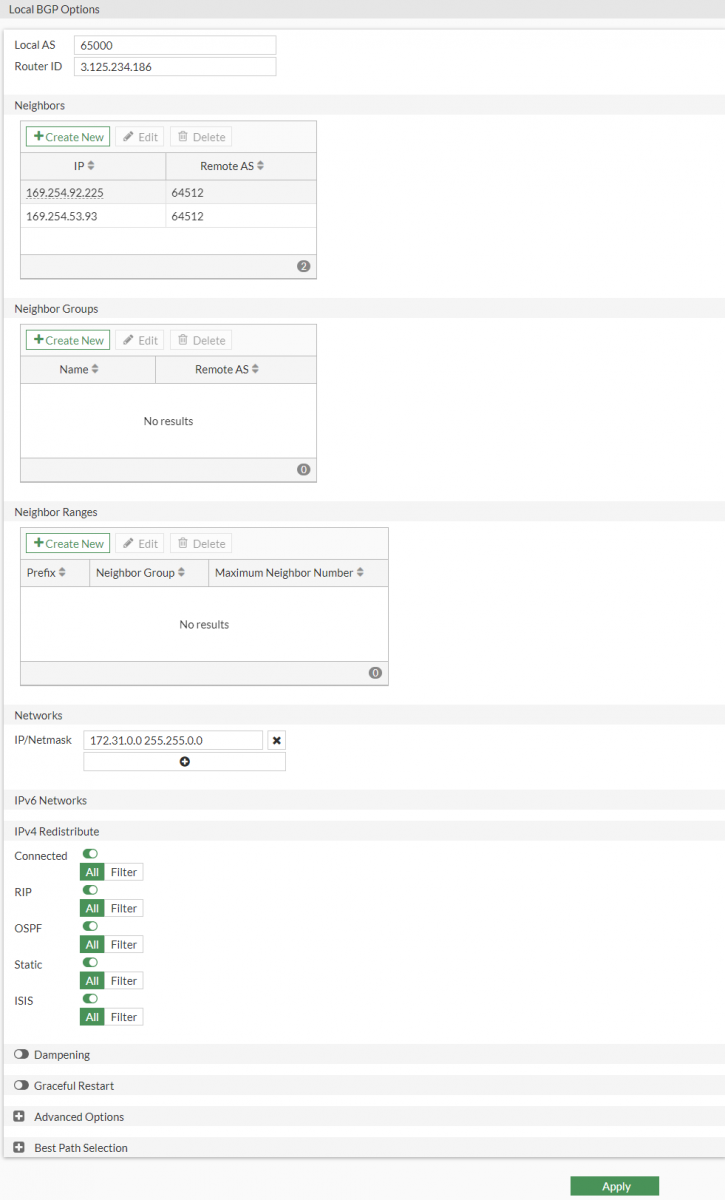
Go to Network > BGP, and configure accordingly to the template conf:
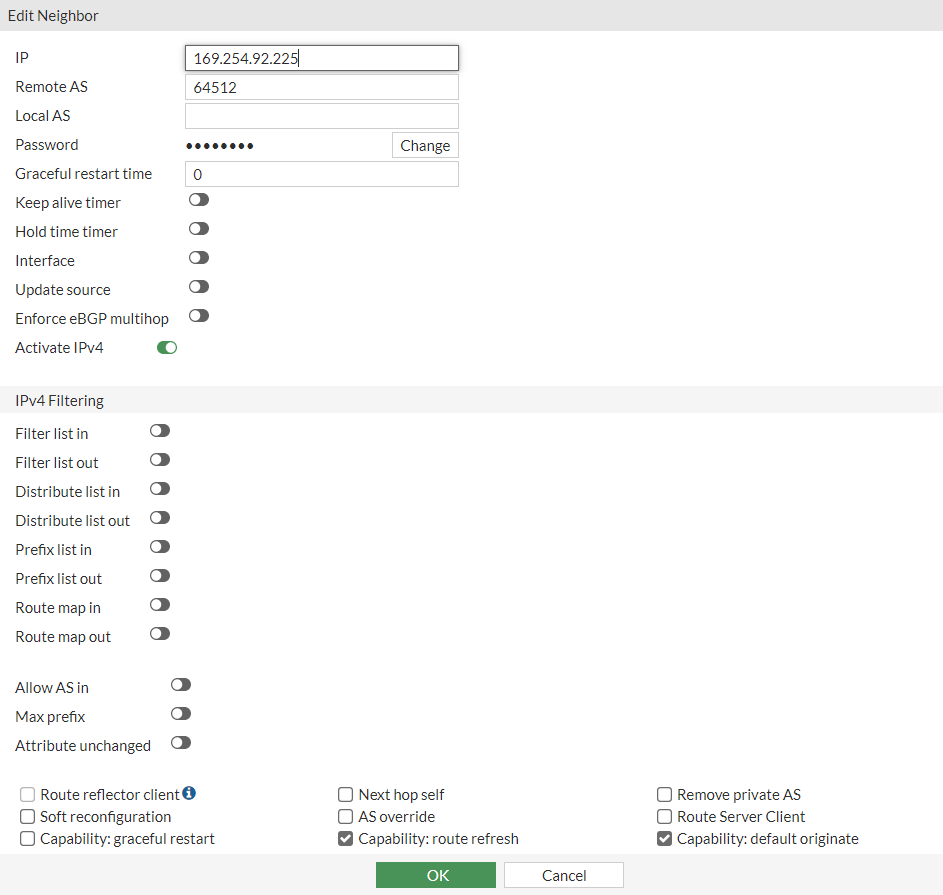
a. Local-AS : 65000 b. Router-ID: 3.125.234.186 c. Click Apply d. Neighbor -> Create New:
IP: 169.254.92.225Remote AS: 64512Click Add/Edit
and
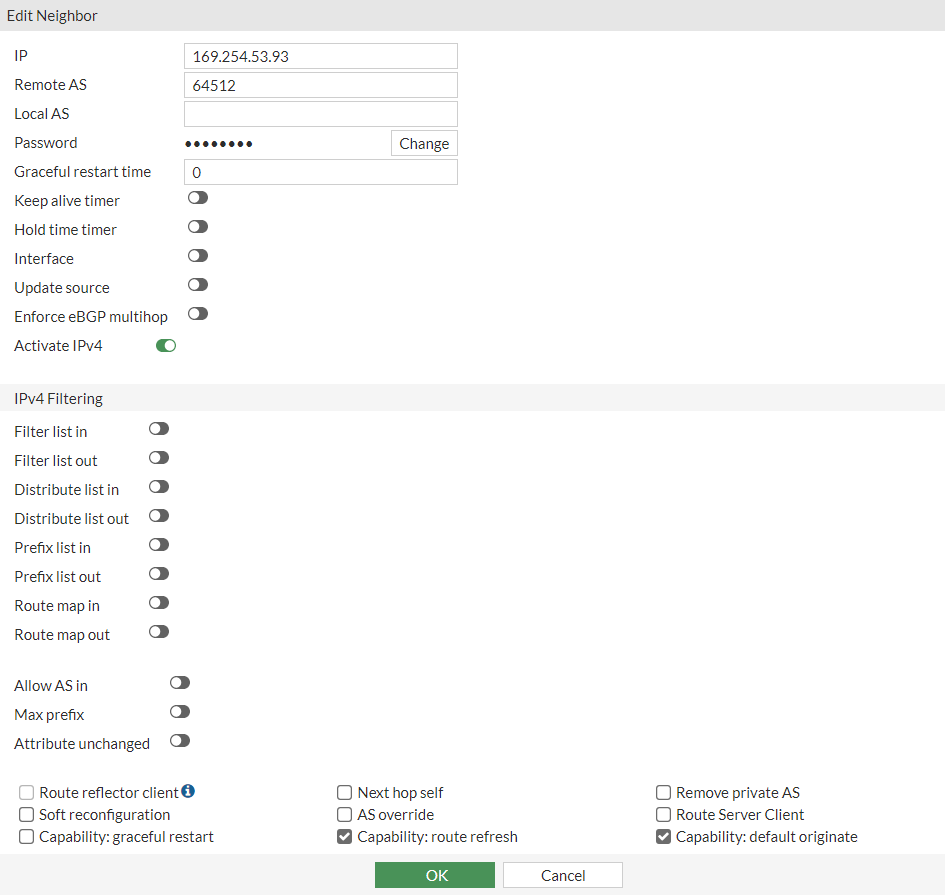
a. Local-AS : 65000 b. Router-ID: 3.125.234.186 c. Click Apply d. Neighbor -> Create New:
IP: 169.254.53.93Remote AS: 64512Click Add/Edit
Now configure the Prefix Lists and Route Maps needed for BGP.
Go to Network > Routing Objects:
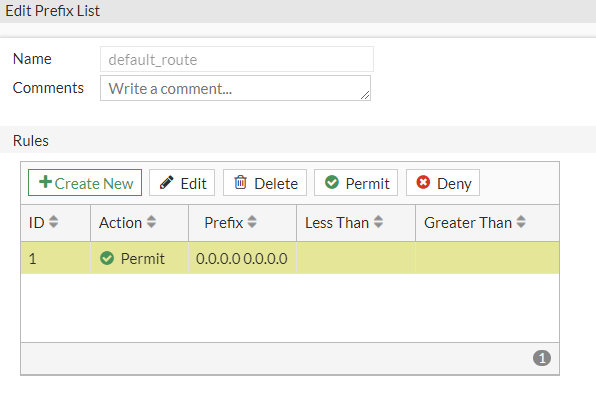
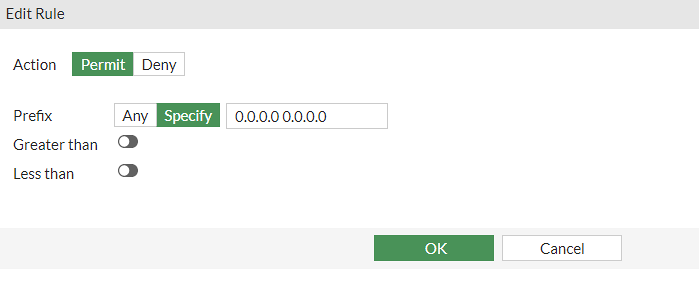
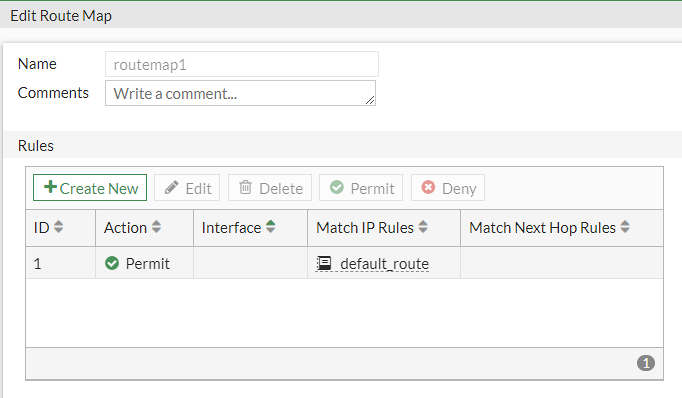
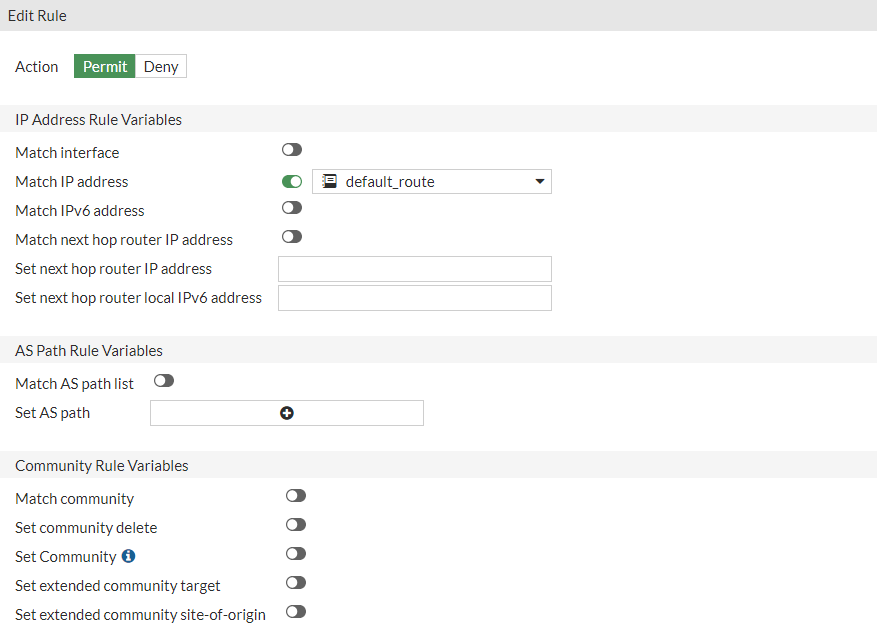
so that at the end we will have this configuration:
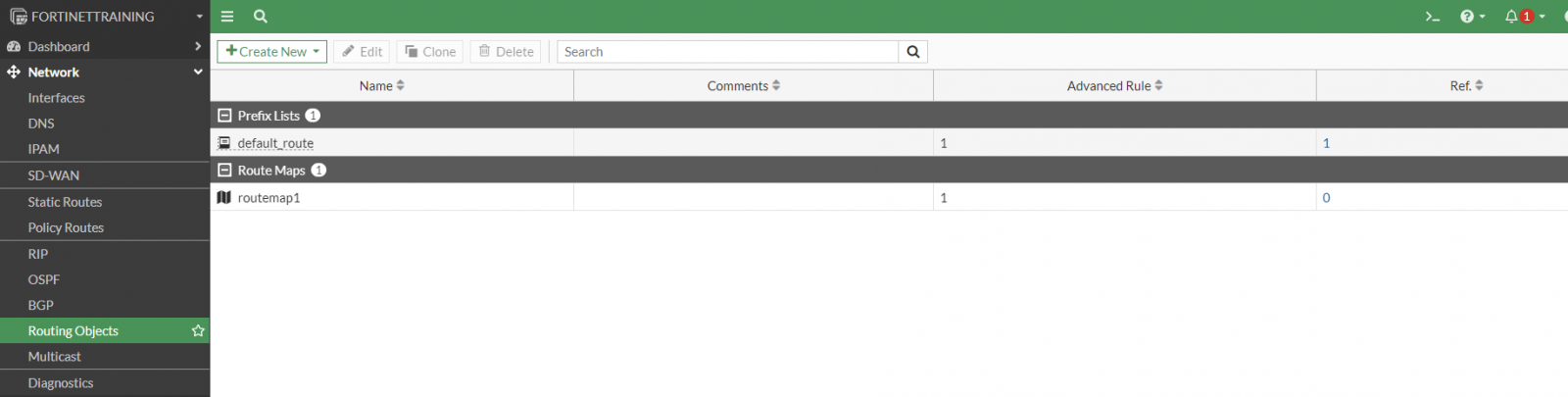
We can also use this script to configure the full BGP section:
config router bgp set as 65000 config neighbor edit 169.254.92.225 set remote-as 64512 end endendconfig router bgp config neighbor edit 169.254.92.225 set capability-default-originate enable endendendconfig router prefix-list edit "default_route" config rule edit 1 set prefix 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 next end endendconfig router route-map edit "routemap1" config rule edit 1 set match-ip-address "default_route" next end nextendconfig router bgp config network edit 1 set prefix 172.31.0.0 255.255.0.0 nextendconfig router bgp set as 65000 config neighbor edit 169.254.53.93 set remote-as 64512 end endendconfig router bgp config neighbor edit 169.254.53.93 set capability-default-originate enable endendend
Configure Firewall policies
We need to create at least two firewall policies permitting traffic from local network to VPN subnet and vice versa:
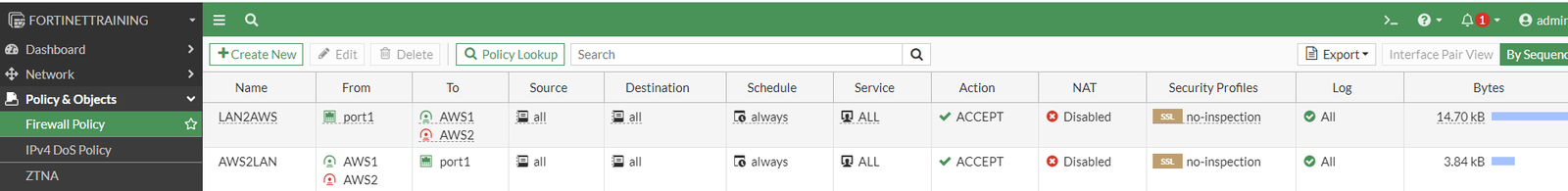
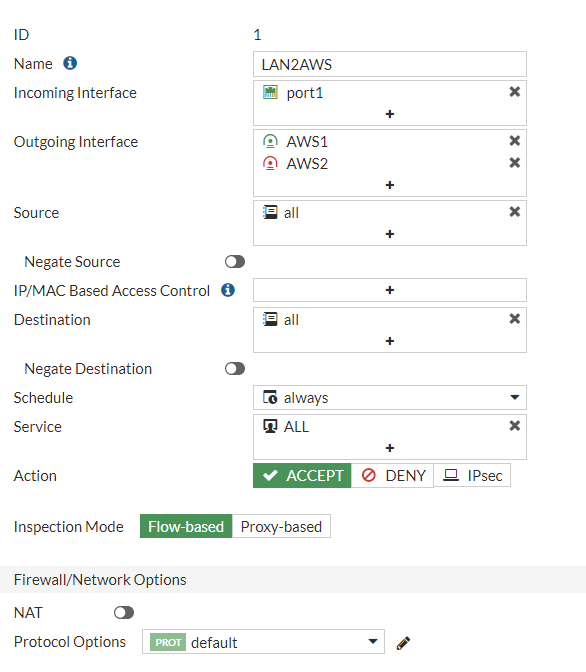
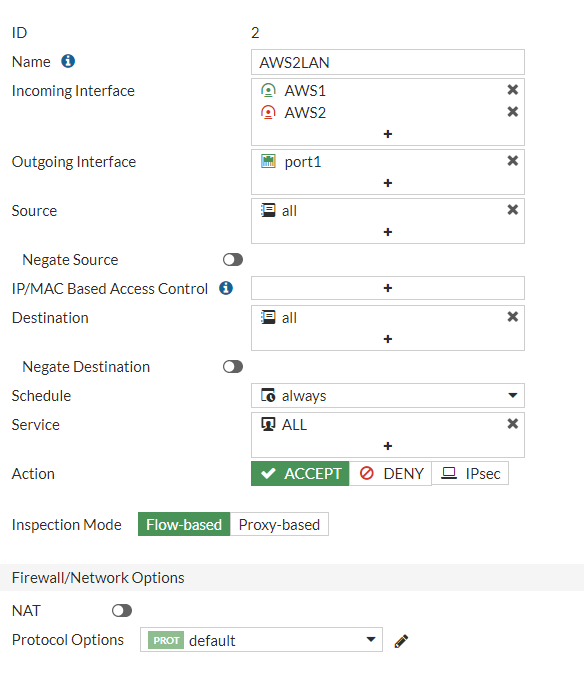
Testing
Now the IPSec tunnels will both be up and running:
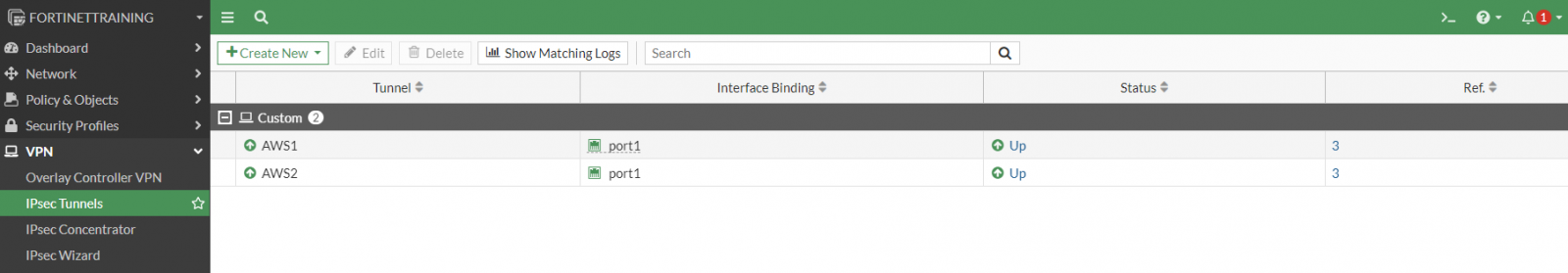
Increase the security in the VPN connection
Now, since AWS side VPN tunnels support better security, we can adjust Fortinet configuration accordingly. We can use:
AES256 instead of AES128
SHA-256 instead of SHA1
Diffie-Hellman group >21 (up to 24) instead of DH2
FortiOS 7.2 supports DH32, but we should use latest version supported by both sides, namely DH21
Let’s adjust Fortinet configuration:
VPN > IPsec Tunnels > edit both tunnels with the new parameters:
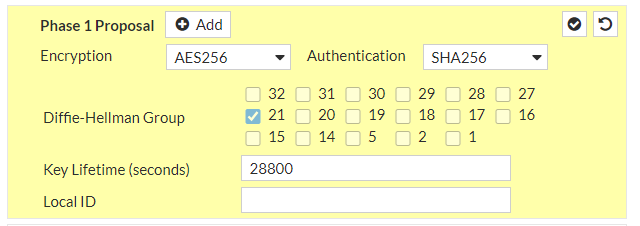
and
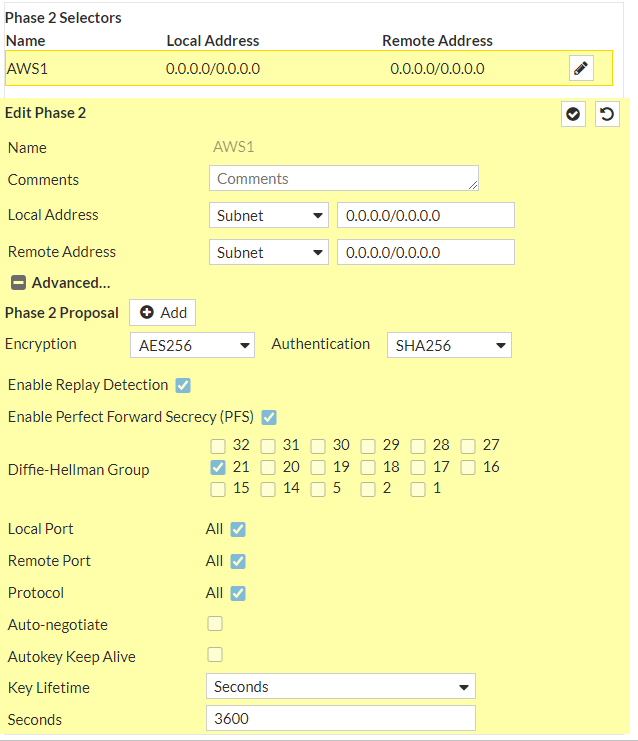
Now the IPSec tunnels will be up and running with maximum security:
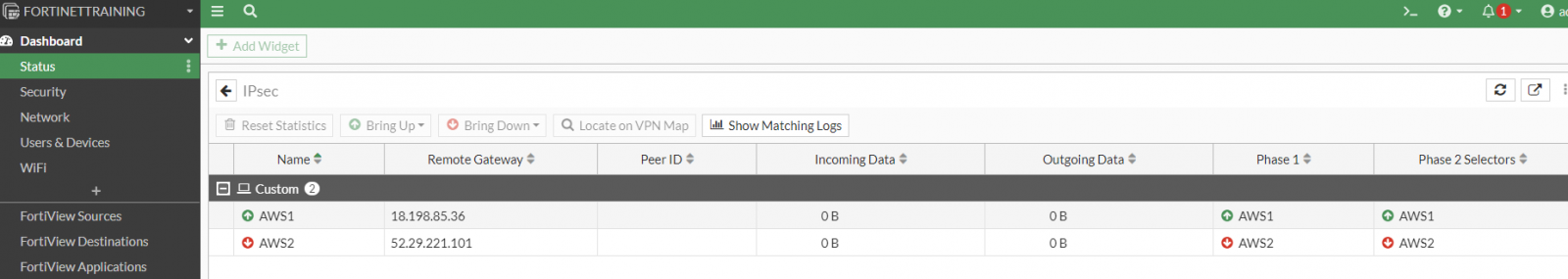
We have done!
For more information and support please contact our UCCS Onboarding Team.
