Description and Architecture
Overview
Imagicle Call Recording is the Imagicle solution for centralized call recording for Cisco UC platforms.
Dedicated to any company that needs to record audio calls either for critical services with legal requirements, for operator training or just to keep track of important calls.
It offers three recording modes:
- Always On, where every call is automatically recorded with no user intervention
- On Demand, letting the user decide when to start conversation recording through a softkey on the IP Phone
- Live Keep, similar to On Demand: when user initiates a recording through phone service Start button, the whole conversation is taken into account and stored.
Imagicle Call Recording can also record calls received on mobile phones (Single Number Reach).
Recorded calls are encrypted by the AES-256 bit algorithm and stored locally on the UC Suite server, where they can be searched and retrieved through the web interface. They can also be automatically saved on an external NAS location.
Technical details
- Supported voice codec: G.711 uLaw/ALaw, G.729A
- Silence suppression is not supported.
- Audio File format: MP3
- Recordings Encryption: AES-256 bit
- Recordings disk occupancy: 300KBytes per minute ⇒ 18 MBytes/hour
Recording audio streams are using the same voice codec of the conversation being recorded. If such codec is not supported by Imagicle Call Recording, Cisco UCM transcoding resources are needed by the recorder SIP trunk to handle them. If the codec is not supported and transcoding resources are not available, the recording fails.
Architecture
Imagicle Call Recording supports multiple technologies to enable audio conversation recording on different phone devices. Each technology enable different features and available recording modes, summarized in the following comprehensive table, highlighting all Imagicle supported recording methods and relevant requirements:
| Built-in Bridge (Cisco UCM) |
Network Based Recording (Cisco UCM + VGW)(8) |
Dial-In (conference recording) |
CUBE(7) SIPREC |
CUBE Network Recording(1) |
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Recording equipments (Phone sets and VGW) |
BiB-enabled(5) IP Phones, Jabber Desktop/Mobile, Webex Teams | BiB-enabled(5) IP Phones, Jabber Desktop/Mobile, Webex Teams; VGW/CUBE | Any phone device | Any phone device; CUBE |
Any phone device; CUBE |
| On-Demand Recording | Yes(4) | Yes(4) | Yes | Yes(2) | Not Supported |
| Always-On Recording | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | |
| Internal (on-net) calls recording | Yes | No | Yes | No | |
| External (off-net) calls recording | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | |
| Recording announcements | Yes(3)(4) | Yes(3) | Yes | Yes(3) | |
| Supports Cisco MRA | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | |
| Supports 3rd party SIP phones | No | No | Yes | Yes | |
| Supports Analog phones | No | No | Yes | Yes | |
| Can provide a periodic recording tone |
Yes | Yes | No | No | |
| Bandwitdh requirements(6) (additional voice streams) |
2 | 2 | 1 | 2 | |
| CUCM requirements | CUCM ver. 8.0(1) or later | CUCM ver. 10.0(1) or later | Conference resources | SIP Trunk to CUBE | |
| Voice Gateway requirements | N/A | ISR-Gen2 (29xx-39xx), IOS 15.3(3)M or higher; ISR-Gen3 (40xx), IOS 15.3(3)S or higher |
N/A | CUBE IOS 15.6(1)T or XE 3.17S or XE 16.3.1 |
(1) Cisco proprietary recording method. See here for more details.
(2) Available through Imagicle Live-Keep mode
(3) Available only to TAPI-enabled Cisco IP phones. Jabber Desktop is supported from rel. 12.9 onward.
(4) Available to Jabber Mobile clients from CUCM rel. 12.5.1 (SU2) onward
(5) The list of BiB-compliant phone devices is available here.
(6) 100Kbps bandwidth required per recording stream, using G.711 codec
(7) Requires as many CUBE-T-STD licenses as the number of expected concurrent recordings; if a redundant CUBE is in place, CUBE-T-RED licenses are additionally required.
Built-in Bridge (phone based) recording
This technology leverages the built-in bridge: a voice-processing component included in almost all Cisco IP phones and softphones. In particular, it allows the "media forking" mechanism described above.
The Built-In Bridge technology can be used for Always On, Live Keep and On Demand recording.
Using the Always-On (automatic) recording mode, when the IP phone line enabled for call recording establishes a conversation, two SIP calls are automatically placed by the CUCM to the Call Recording application through a standard SIP Trunk.
Each call carries a one-way RTP audio stream by one of the involved parties. Both RTP streams are originated by the IP phone, leveraging the phone built in bridge.
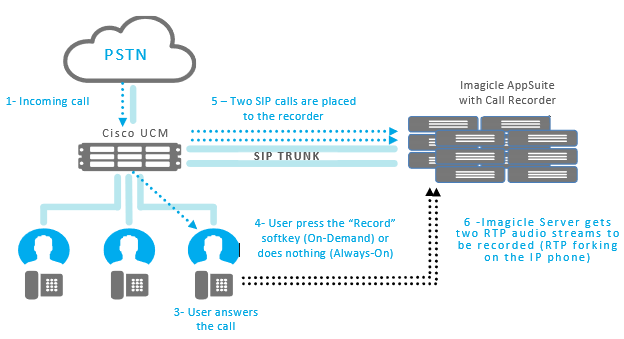
Similarly, if the phone is configured for On-Demand recording ("selective recording"), the user can start recording the established call, at any time, simply pressing the programmed "Record" softkey or button on his/her IP Phone. Depending on the phone model and UCM version, also the "Stop Record" recording softkey is available on the phone (otherwise the recording stops when the conversation is ended).
Built-In Bridge recording requires CUCM rel. 8.x or higher for Always On and 9.x or higher for On Demand.
Network (gateway based) recording
The Cisco Network-Based Recording leverages the Cisco Voice Gateway capabilities to fork media, sending the audio streams to the Call Recording SIP application.
This technology can be used for Always On, On-Demand and Live Keep recording.
This method is recommended when the IP phone subjected to recording is configured for Single Number Reach or calls are transferred to an external fixed/mobile number. In this case, two recording RTP streams are originated from the gateway, each including a call party. If the call is answered from IP Phone, then recording is automatically switched to Built-in-Bridge method.
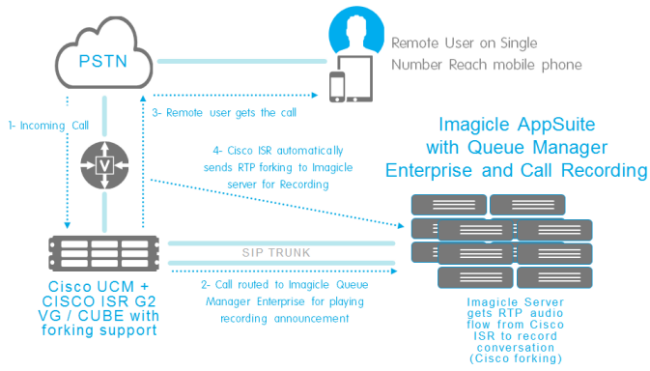
This mode requires the use of CUCM rel. 10.x or higher and Cisco Voice Gateway ISR-Gen2 Gateways (29xx-39xx), IOS 15.3(3)M or higher, which can be configured in Voice Gateway or CUBE mode. See https://developer.cisco.com/site/uc-manager-sip/documents/requirements/ for details.
Design considerations
Choosing the recording technology
The two mentioned recording technologies can also be combined together, in the same environment, to better fit your call flow scenario. See the PBX configuration chapter or the Cisco documentation to understand how to combine them.
In facts, if both the technologies are enabled on CUCM, the PBX chooses call by call for the specific conversation the best technology to record it.
Imagicle Call Recording manages both of them without any configuration change.
However, when designing you recording environment consider that:
- Only built-in bridge recording allows to record internal on-net calls (between two extensions) that do not traverse any voice gateway or CUBE device.
- Only network recording allows to record incoming calls answered by remote devices (mobile or PSTN phones) when using CUCM Single Number Reach feature (Remote Device profile).
- Network Based Recording does not support conference calls recording.
- Network Based Recording does not support recording if Voice Gateway is running a TCL IVR application with the exception of survivability.tcl, which is supported with NBR.
- Media mixing on gateway-forked streams is not supported
Telephony and network requirements
- Transcoding resources: if you need to record conversations established with codecs other than G.711 and G.729A, you need to provide enough hardware transcoding resources to the Imagicle Call Recording SIP trunk (specifying a suitable Media Resource Group List). Otherwise, ensure to disable unsupported codec following the instructions in PBX configuration page.
- Bandwidth considerations: as described above, the media forking technology involves two one-way audio calls (and audio streams) to the call recording server. Therefore, additional bandwidth is required in upload from the recording device (telephone or voice gateway) to the Imagicle call recording server. This is important if you plan to manage a multi-site scenario with a centralized recording server.
The upload bandwidth requirement depends on the adopted codec but is roughly twice the bandwidth of a regular call, that is:- G.711: about 175 Kbps for each conversation being recorded.
- G.729: about 62 Kbps for each conversation being recorded.
- Supported phone models: see the Cisco documentation for the latest available list of supported models, and their capabilities.
- The remote party number information is available with CUCM 8.5(1) and higher versions.
- Supported voice gateways (for network recording technology only):
- UCM 10.0 or higher
- Voice gateways or CUBE meeting the requirements documented by Cisco.
- If you plan to export recordings to a remote storage, additional bandwidth is required for the file transfer between the Imagicle call recording server and the remote network folder. Such bandwidth actually depends on the volume of recorded traffic (maximum 20MB/hour for each recording licensed channel).
- High-Availability deployments involving multiple Imagicle servers require enough bandwidth between each Imagicle node in order to synchronize the audio recording files. Such bandwidth actually depends on the volume of recorded traffic (maximum 20MB/hour for each recording licensed channel).
Support for Cisco MRA devices (Cisco Collaboration Edge)
| IP Phone | Jabber Desktop (Windows / Mac) |
Jabber Mobile (iOS / Android) |
Webex Desktop (Windows / Mac) |
|
| Built-in Bridge - On Demand (requires TAPI control) |
YES (1)(2) | YES (1)(2) | YES (2)(3)(4) | YES (2)(4) |
| Built In Bridge - Always On | YES (1)(2) | YES (1)(2) | YES (1)(2) | YES (1)(2)(3) |
| NBR Recording - On Demand (requires TAPI control) |
YES (2) | YES (2) | YES (2)(3)(4) | YES (2)(4) |
| NBR Recording - Always On | YES (2) | YES (2) | YES (2) | YES (1)(2)(3) |
(1) Requires Expressway ver. X8.11.4 or higher and CUCM 11.5 (SU5) or higher
(2) Call Recording announcements requires Expressway ver. X12.6.2 or higher
(3) Requires CUCM 12.5.1 (SU2)
(4) Requires the gadget for Jabber/Webex to start/stop the recording. See here for the further details.
Dial-In mode
In addition to the two Cisco technologies mentioned above, a third recording technique (hereafter named "Dial-In") is possible with Imagicle Call Recording. This is an "On-Demand" recording mode that can be used for devices that do not support the built-in bridge and network recording (analog phones, 3rd party SIP phones, etc).
This mode involves a 3-parties conference call engaged by the operator that includes both the remote party and the recording application.
Manual Dial-In
How it works
- The operator establishes a conversation with the remote party (incoming or outgoing call).
- The operator initiates a conference with the recorder, placing an invitation call to recorder (calling the pilot number associated to the recorder, for instance 8500).
The remote party is automatically put on hold. - The recorder answers the call and plays a beep (recording tone confirmation).
- The operator completes the conference between the remote party, the call recorder and the operator himself. The recorder will silently record all the conversation.
- The operator hangs up the call and the conference.
Limitations
- This recording mode is initiated manually (on-demand), therefore this is not suitable for "always-on" scenarios that require the automatic, transparent recording.
- The remote party number is not available, therefore it will be blank in the recordings list, in the recording filenames, etc.
- The call direction cannot be determined, therefore it will appear blank in the recordings list.
Technical considerations
- The recording phone and the conference bridge must be able to establish the call with the Call Recording service, using one of the supported codecs (G.711, G.729A).
- The recording phone must be able to do at least 3-parties audio conferences.
- The required bandwidth to/from the recorder is the same of a regular phone call.
Automated Dial-In
Available since 2018.Winter.1, this mode allows the operator to trigger the Dial-In recording mode by just pressing a Service Button URL configured on the IP Phone.
How it works
- The operator establishes a conversation with the remote party (incoming or outgoing call).
- The operator presses a Service Button URL available on the IP Phone.
- Imagicle Call Recording:
- Places an invitation call to Call Recording service from the operator's IP Phone. The remote party is automatically put on hold
- Answers the call and plays a beep (recording tone confirmation)
- Completes the conference between the remote party, the Call Recording service and the operator
- Silently records all the conversation
- The operator hangs up the call and the conference.
Advantages
Compared to Manual Dial-In, Automated Dial-In removes two limitations and provides:
- The remote party number
- The call direction
Limitations
- This recording mode is on-demand only, therefore it is not suitable for "always-on" scenarios that require automatic, transparent recording.
- This recording mode is compatible only with Cisco IP Phone models that are CTI controllable and support the Service Button URL.
- This recording mode is not compatible with overlapping dialing plans
Technical considerations
- Imagicle Call Recording requires CTI (TAPI) control on operators phones.
- The recording phone and the conference bridge must be able to establish the call with the Call Recording service, using one of the supported codecs (G.711, G.729A).
- The recording phone must be able to do at least 3-parties audio conferences.
- The required bandwidth to/from the recorder is the same of a regular phone call.
Free-Seating
Imagicle Call Recording supports the "free seating" scenario: nomadic users can work on different desks/locations using the Extension Mobility feature of Call Manager.
To enable call recording in such scenario you only need to:
- Assign to the Application Suite user the DN of the Extension Mobility Profile
- Configure the device profile as described in the PBX configuration document page to enable call recording on the phone line.
Data processing and Storage
When a recording completes, the service both stores some data in the application suite database (recording index) and in the local file system (MP3 audio file). The main processing steps are:
Recording of 2 audio streams ⇒ Mix and MP3 compression ⇒ AES Encryption ⇒ DB Indexing
The encrypted recordings are saved into a subfolder of the installation folder, in particular: ...\StonevoiceAS\Apps\Recorder\Records
Files are further subfolder by year, month and date:
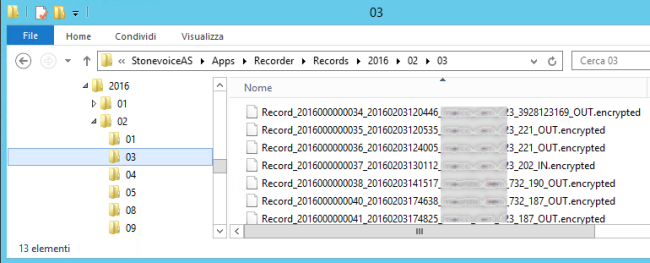
The filename of each recording include some useful information, in particular:
- The (sequential) Record Id
- A 14 digits timestamp (yyyymmddHHmmss)
- The recording username (as configured in IAS)
- The recording extension
- The remote party number
- The call direction (IN/OUT)
Hint: please contact the Imagicle support service if you need to move recordings to another folder or disk unit
Disk Occupancy
The disk occupancy of each recording is about 16 MB per hour.
Consider that when sizing the server disk, the overall occupancy should be calculated accordingly with the estimated traffic figure and planned data retention. In facts, the disk space needed to store the call recordings depends on:
- The number of agents
- The number of calls per hour
- Average call duration
- how log you want to store the recorded calls
Imagicle provides an Excel worksheet which allows you to calculate the required disk space.
Following some examples of occupancy figures, for different recording scenarios.
| Recording Scenario | Simultaneous conversations (agents) |
Daily recording |
Data Retention (months) |
Necessary disk space (GB) |
| Help Desk (8x6) |
4 | 6 | 6 | 54 |
| 20 | 6 | 6 | 270 | |
| Emergency service (24x7) |
2 | 2 | 48 | 90 |
| 10 | 2 | 48 | 450 | |
| Teleselling (8x6) |
8 | 6 | 12 | 216 |
| 30 | 6 | 12 | 810 | |
| 60 | 6 | 12 | 1.620 |
Hardware Requirements
In our Storage Calculator, we also display the amount of Calls Per Second (CPS) globally engaged by Call Recording users. CPS is calculated for both channel-based license (ERLANG calculation applied) and user-based license. Please make sure to keep CPS value below 3, to avoid overloading Imagicle recording engine with too many concurrent recording requests. If your calculation returns a CPS value over 3, please contact Imagicle to learn about specific hardware requirements to fulfill your traffic needs.
MP3 format details
Recordings are compressed and stored in MP3 format, with a constant bit rate of 32 kbps.
The following table contains the list of the ID3 tags valued in the MP3 recording files and their meaning.
| Content |
User friendly |
ID3 tag name | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Record ID | Title | #TIT2 Title, songname or content description |
2019000001344 |
| Owner IAS username |
Copyright | #TCOP Copyright |
john_doe |
| Owner first & last name |
Composers | #TCOM Composer |
John Doe |
| Owner extension number | Contributing Artists | #TPE1 Lead performers/Soloists |
2501 |
| Remote number | Album Artists | #TPE2 Band/orchestra/accompaniment |
+1555820132 |
| Associated screen recording id (If Screen Recording add-on is enabled | Conductors |
#TPE3 |
EVT_63120430e0e4d3 |
| Start date-time | Subtitle (ISO format, UTC) |
#TIT3 |
2019-10-04T14:52:29 |
| Start date-time |
Recording time |
#TYER #TIME |
2019 04/10/2019 16:52 |
| Duration | Length/Duration | #TLEN Length (in ms) |
138000 |
| Call direction (IN/OUT) | Genre | #TCON Content type/Genre |
OUT |
|
||
| This article was: |
| Attached files | |
| Imagicle Call and Screen Recording Channel and Storage Calculator-rev2.xlsx (98 kb) | |
| Prev | Next | |
| Configuration Task List | License Activation |
